In the realm of research, qualitative methods have emerged as powerful tools for understanding complex social phenomena. Unlike quantitative methods, which focus on numerical data, qualitative research delves into the richness of human experience, providing depth and insight that numbers alone cannot convey. This article explores effective qualitative research methods and their real-world applications, highlighting their relevance, practicality, and potential for impactful results.
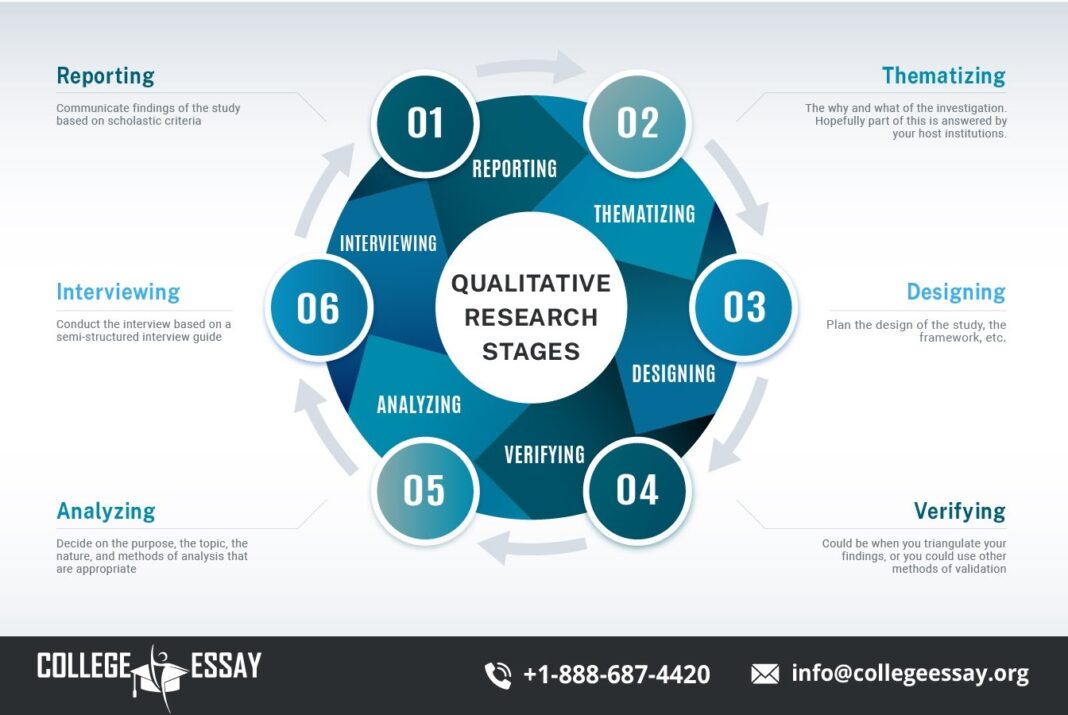
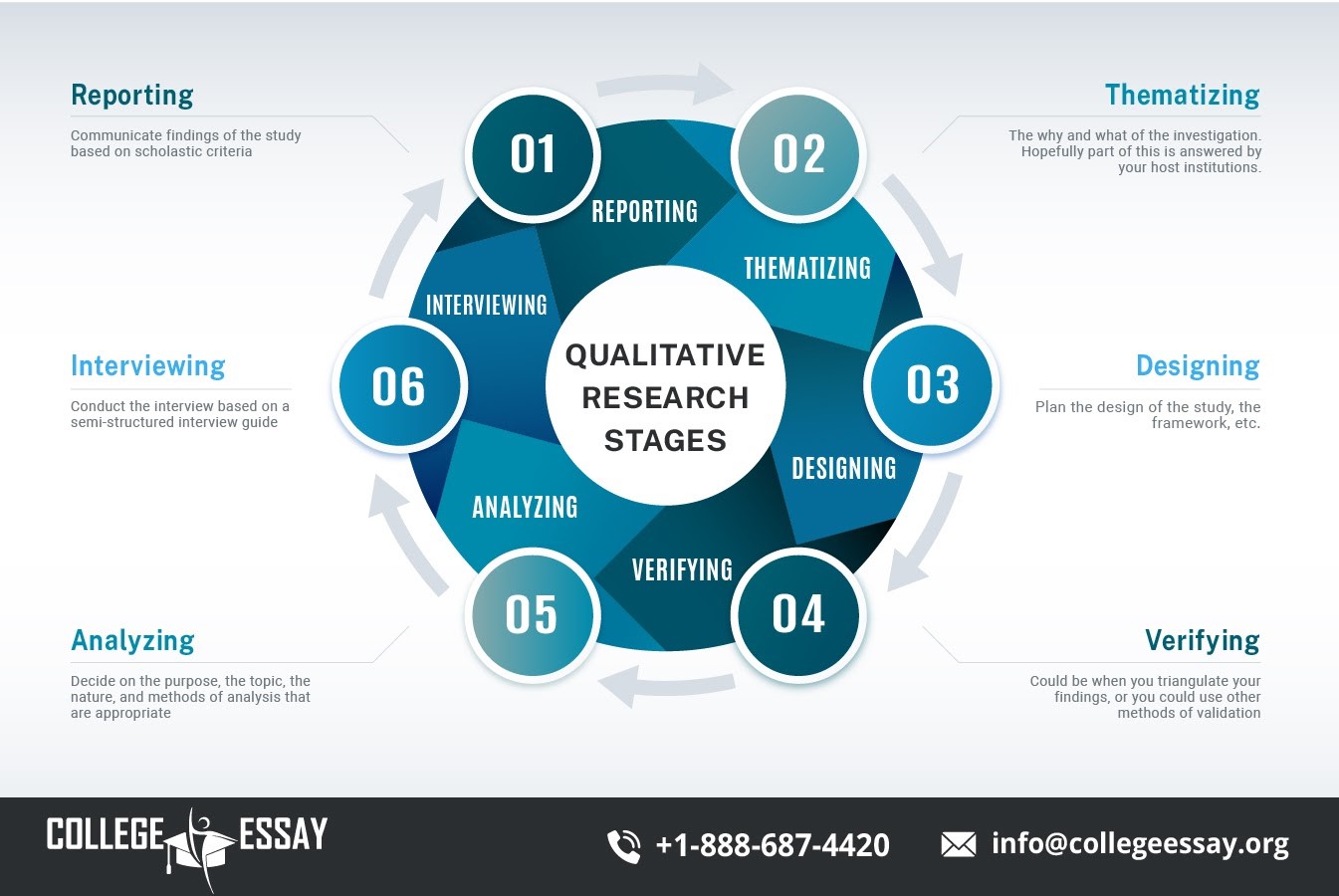
Understanding Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is inherently exploratory, aimed at gaining a deeper understanding of human behavior, motivations, and interactions. It is particularly effective in contexts where the objective is to uncover trends, patterns, and deeper insights rather than to measure or quantify specific variables. Common qualitative methods include interviews, focus groups, ethnography, and case studies, each offering unique advantages depending on the research goals.
Key Qualitative Research Methods
1. In-Depth Interviews
In-depth interviews involve direct, one-on-one engagement between the researcher and the participant. This method allows for deep exploration of individual perspectives, providing nuanced insights into personal experiences and viewpoints. In-depth interviews are particularly useful in contexts where personal stories and detailed narratives are crucial, such as in psychology, sociology, and market research.
Real-World Application: In healthcare, in-depth interviews with patients can uncover personal experiences with illness and treatment, leading to improved patient care strategies and healthcare policies.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups gather a small group of participants to discuss a specific topic under the guidance of a facilitator. This method leverages group dynamics to generate a range of views and ideas, revealing collective opinions and diverse perspectives. Focus groups are effective for exploring community attitudes, product feedback, and social issues.
Real-World Application: Companies often use focus groups to test new products or services, gathering feedback that can inform product development and marketing strategies.
3. Ethnography
Ethnography involves immersive observation and participation within a community or culture. Researchers engage with participants in their natural environments, often over extended periods, to gain a holistic understanding of their behaviors, rituals, and interactions. This method is valuable in anthropology, education, and organizational studies.
Real-World Application: Ethnographic research in educational settings can reveal insights into classroom dynamics, teaching methods, and student interactions, informing educational reforms and teaching practices.
4. Case Studies
Case studies involve an in-depth analysis of a single case or a small number of cases. This method is ideal for exploring unique or complex phenomena in detail, providing comprehensive insights into specific instances. Case studies are widely used in business, law, and social sciences.
Real-World Application: In business, case studies can analyze successful or failed companies, offering valuable lessons and strategies for other organizations.
Ensuring Rigor in Qualitative Research
To ensure the credibility and reliability of qualitative research, it is essential to maintain rigor through systematic data collection and analysis. Key strategies include:
- Triangulation: Using multiple methods or sources to validate findings.
- Member Checking: Seeking feedback from participants on the accuracy of the findings.
- Thick Description: Providing detailed, contextualized descriptions of the research setting and participants.
- Reflexivity: Researchers critically reflecting on their own biases and influence on the research process.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in qualitative research. Researchers must obtain informed consent, ensure confidentiality, and be sensitive to the potential impact of their work on participants. Maintaining ethical standards not only protects participants but also enhances the integrity and trustworthiness of the research.
Integrating Qualitative Research into Practice
The true value of qualitative research lies in its application to real-world challenges. By translating insights into actionable strategies, qualitative research can drive meaningful change in various fields. For instance:
- Healthcare: Patient narratives can inform patient-centered care models, improving treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
- Education: Understanding student experiences can lead to more effective teaching methods and inclusive educational policies.
- Business: Consumer feedback can guide product innovation and marketing strategies, enhancing customer satisfaction and business success.
- Social Policy: Insights into community needs and perspectives can shape more effective and equitable policies.
Conclusion
Qualitative research methods, when applied effectively, offer profound insights into human experiences and social phenomena. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, these methods can drive significant advancements across various fields. For researchers and practitioners alike, embracing qualitative research can lead to deeper understanding, more informed decision-making, and ultimately, more impactful and sustainable solutions.