In recent years, decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) have emerged as a transformative approach to conducting clinical research, revolutionizing traditional methodologies and improving patient accessibility and participation. This article explores the growing momentum behind decentralized clinical trials, highlighting their benefits, technological advancements driving adoption, regulatory considerations, and future implications for the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries.
Understanding Decentralized Clinical Trials
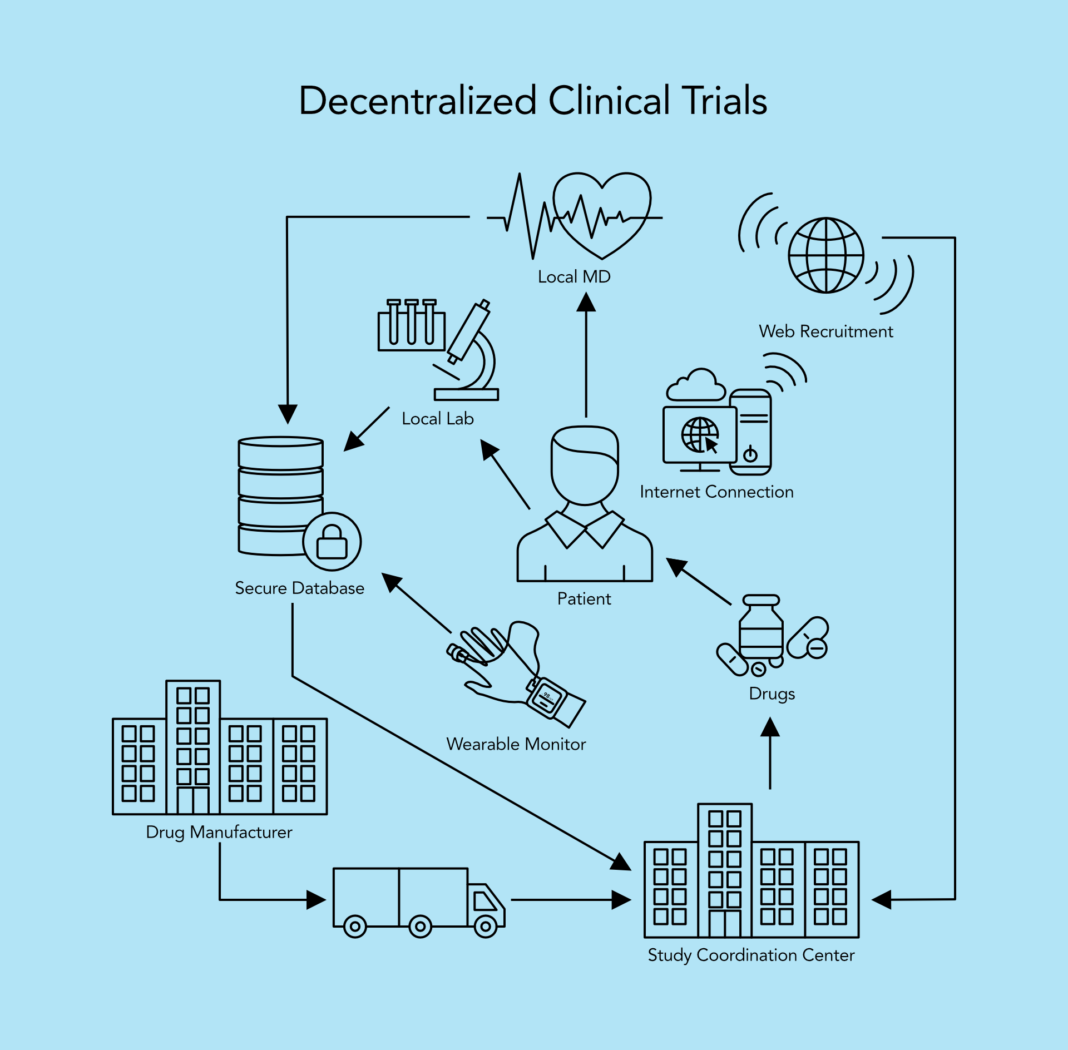
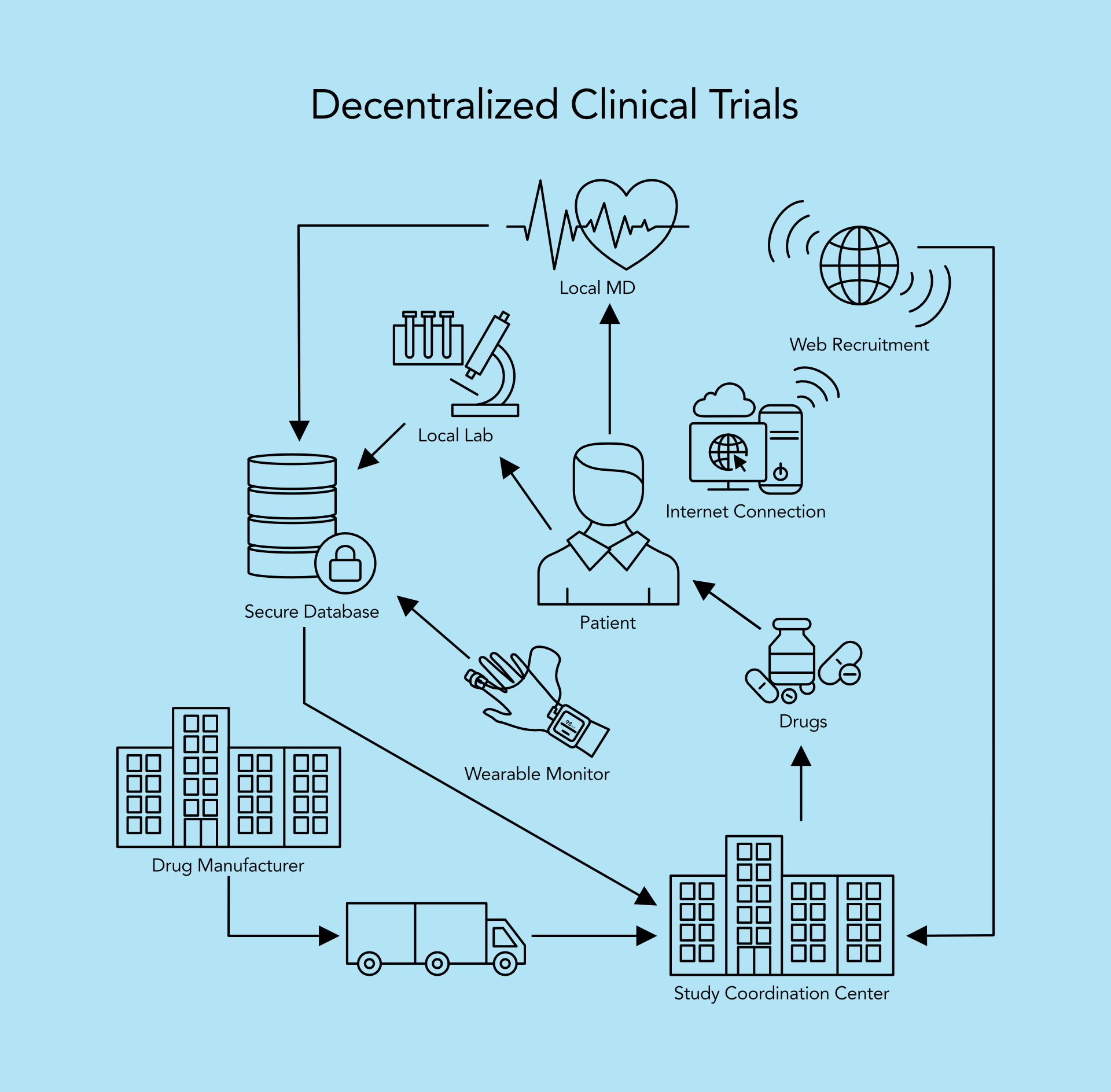
Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) represent a departure from traditional, site-centric models by leveraging digital health technologies and remote monitoring to conduct aspects of the trial outside of conventional clinical settings. Key characteristics of DCTs include:
- Remote Participant Engagement: Utilizing telemedicine, mobile health apps, and wearable devices to enable remote participant recruitment, consent, and data collection.
- Virtual Trial Sites: Implementing virtual or hybrid trial designs that decentralize study activities across multiple locations, including participants’ homes and local healthcare facilities.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Continuous remote monitoring of participant data through digital platforms to ensure data integrity, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
Advantages of Decentralized Clinical Trials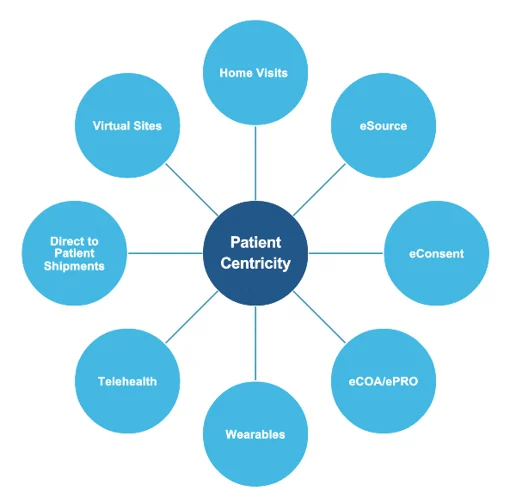
- Enhanced Patient Access and Diversity:
- DCTs broaden access to clinical trials by overcoming geographical barriers and allowing participation from diverse patient populations, including those in rural or underserved areas.
- Improved Participant Retention:
- By reducing the burden of frequent clinic visits and offering flexible scheduling, DCTs enhance participant retention rates and compliance with study protocols.
- Efficient Data Collection and Monitoring:
- Real-time data collection through digital health technologies accelerates data analysis, enhances study efficiency, and facilitates early identification of adverse events.
- Cost Efficiency and Timeliness:
- Reduced overhead costs associated with site management and patient travel contribute to overall cost savings and expedite trial timelines, potentially accelerating drug development.
Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring Solutions:
- Integration of telehealth platforms enables virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and secure communication between participants and healthcare providers.
- Wearable Devices and Digital Biomarkers:
- Adoption of wearable devices for continuous monitoring of vital signs, physical activity, and biomarkers enhances data accuracy and provides real-world insights into patient health.
- Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems:
- Advanced EDC systems facilitate secure data collection, storage, and analysis while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and data privacy standards.
Regulatory Considerations and Guidelines
- FDA and Global Regulatory Frameworks:
- Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA), have issued guidance and frameworks to support the implementation of DCTs.
- Data Security and Privacy:
- Compliance with data security regulations (e.g., GDPR) and protection of patient privacy are paramount in decentralized trials, necessitating robust data management strategies and secure technology platforms.
Future Implications and Industry Outlook
- Expansion of Hybrid Trial Designs:
- Hybrid trial models combining elements of traditional and decentralized approaches are expected to proliferate, catering to diverse study requirements and patient demographics.
- Collaborative Partnerships and Stakeholder Engagement:
- Industry collaboration between pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), technology providers, and healthcare stakeholders will drive innovation and adoption of DCTs.
- Patient-Centric Approach:
- Emphasis on patient-centricity in clinical trial design and execution will continue to shape the evolution of decentralized models, prioritizing patient convenience, safety, and engagement.
Conclusion
Decentralized clinical trials represent a paradigm shift in clinical research, offering significant advantages in patient access, data quality, and study efficiency. As digital health technologies evolve and regulatory frameworks adapt, the momentum behind DCTs is expected to accelerate, transforming the landscape of clinical trials and drug development.
For stakeholders in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries, embracing decentralized trial methodologies presents opportunities to enhance research outcomes, optimize resource utilization, and ultimately deliver innovative therapies to patients more efficiently and effectively. Stay informed about the latest advancements and regulatory updates in decentralized clinical trials to capitalize on this transformative approach to clinical research.